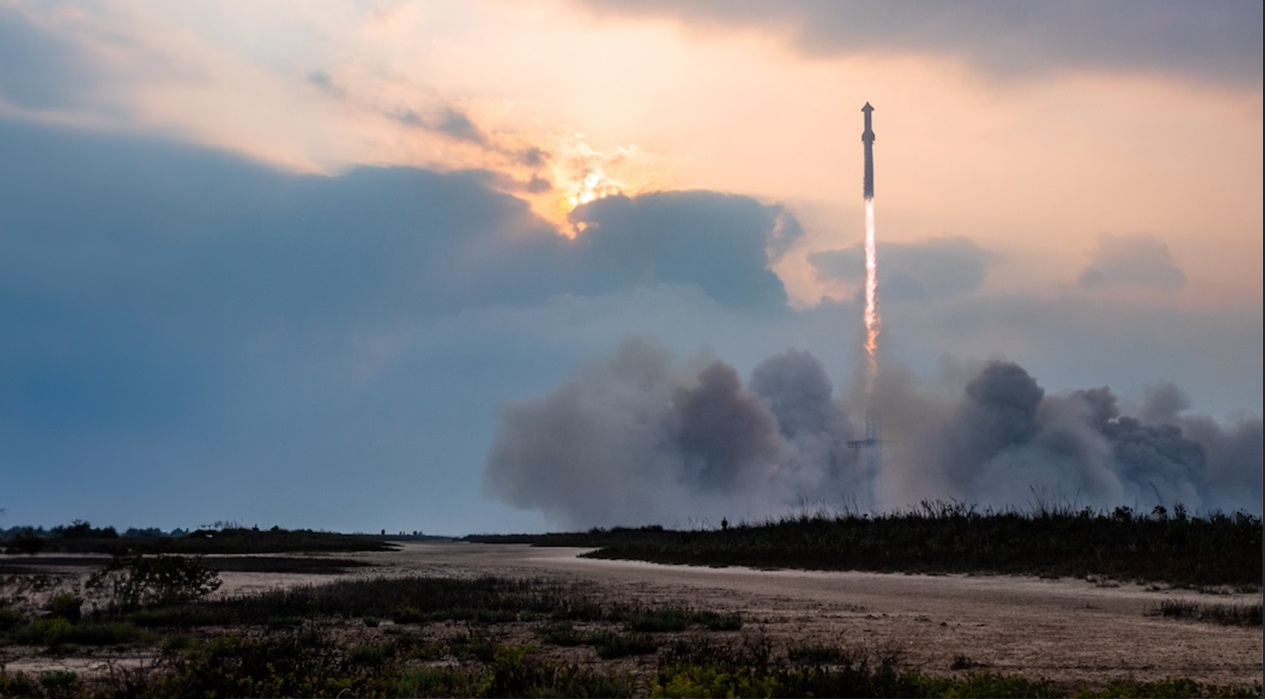
SpaceX Starship launches on nail-biting 4th test flight of world’s most powerful rocket
SpaceX’s Starship program continues to make strides with its fourth test flight (Flight 4) on June 6, 2024. This launch marked a significant step towards the goal of a fully reusable launch vehicle for deep space missions.
Key achievements of Flight 4
- Successful soft splashdowns: Both the Super Heavy booster (Booster 11) and Starship upper stage (Ship 29) achieved soft splashdowns in the ocean, a first for the program.
- Deeper reentry: The mission aimed to push Starship deeper into the atmosphere during reentry, a crucial test for future missions.
- Improved turnaround time: Flight 4 came just 84 days after Flight 3, demonstrating SpaceX’s ability to learn and adapt quickly.

Challenges and upcoming milestones
- Heat shield damage: The Starship upper stage experienced heat shield damage during reentry, highlighting the need for further refinement.
- Super Heavy engine issues: One engine on the booster and several on the upper stage didn’t fire as expected, requiring further investigation.
- Next steps: SpaceX is targeting a more ambitious goal for Flight 5 – catching the Super Heavy booster using the launch tower’s “chopsticks.”
NASA’s Artemis program and Starship
- Starship is central to NASA’s Artemis program, aiming to return humans to the Moon in 2026.
- Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of the Human Landing System program at NASA, praised the progress made and highlighted the successful propellant transfer test during Flight 3. This capability is vital for Starship’s refueling strategy in space.
- Collaboration with SpaceX is ongoing, with NASA astronauts providing valuable feedback on the Starship’s human-rated design.
Future outlook
- The success of Flight 4, combined with a faster turnaround time, could pave the way for a quicker announcement of Flight 5.
- Regulatory hurdles are being addressed, with the FAA approving SpaceX’s plans for Starship entry scenarios.
- Continued testing will be crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the success of future missions, including NASA’s Artemis 3.
Overall, Flight 4 represents a significant leap forward for the Starship program, bringing it closer to its goal of becoming a key player in deep space exploration.